Best Small CNC Machining Machines for Industrial Applications in 2025
Are you looking for the perfect small CNC machine for your industrial applications? Finding the right balance between size, precision, and functionality can be challenging. In today’s article, we’ll explore the best small CNC machining machines that deliver industrial-grade performance without consuming excessive floor space—perfect for specialized manufacturing operations including precision component production for the new energy vehicle (NEV) industry.
Introduction: The Rising Importance of Small CNC Machines
Small CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized modern manufacturing by bringing precision automation to compact spaces. These powerful tools have become essential for businesses looking to maintain competitive edge in specialized industries like automotive, aerospace, and particularly the rapidly growing NEV sector.
Unlike their larger counterparts, small CNC machines offer remarkable flexibility and cost-effectiveness without compromising on precision. They’re particularly valuable for high-precision applications where tight tolerances and consistent quality are non-negotiable—such as in the production of electrical components, circuit boards, and specialized metal parts.
As we move further into 2025, the demand for these compact powerhouses continues to grow. According to recent market analysis, the small CNC machine market is projected to reach $3.5 billion globally this year, with a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% expected through 2028.
For companies specializing in precision manufacturing, like those in the busbar processing industry, small CNC machines offer the perfect combination of accuracy, repeatability, and space efficiency. Let’s explore the top options available today.
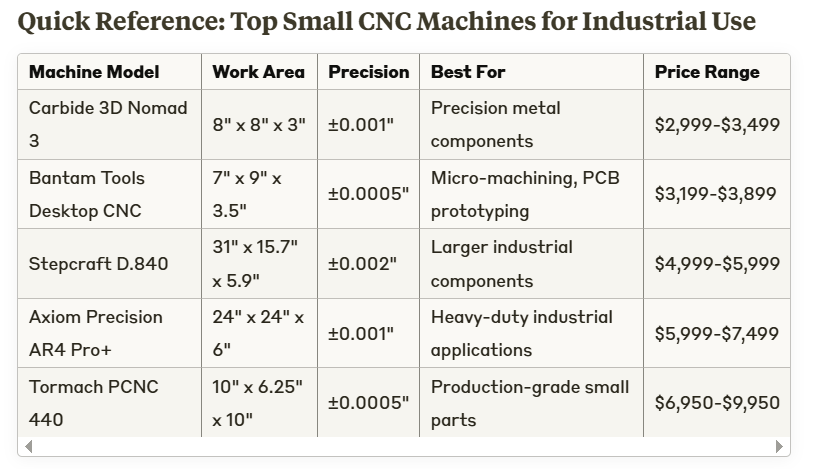
Top 5 Small CNC Machines for Professional and Industrial Use
Carbide 3D Nomad 3: Compact Excellence for Precision Metal Work
The Carbide 3D Nomad 3 stands out as a top contender in the small CNC machine market, particularly for operations requiring exceptional precision in a compact footprint. Despite its small size, this machine delivers industrial-grade performance that makes it suitable for manufacturing critical components.
Key advantages of the Nomad 3 include:
- Enclosed design that contains debris and reduces noise—perfect for cleaner manufacturing environments
- Cast iron frame that minimizes vibration and ensures consistent cutting precision
- Automatic tool length probing for enhanced accuracy and reduced setup time
- Compatibility with a wide range of materials including aluminum, brass, steel, and high-performance plastics
The Nomad 3 excels in applications where tight tolerances are critical, such as in the production of electrical connectors and components for the NEV industry.
Bantam Tools Desktop CNC Milling Machine: Micro-Precision Champion
When it comes to micro-machining and ultra-precise applications, the Bantam Tools Desktop CNC delivers exceptional performance in an incredibly compact package. This machine is designed specifically for applications where precision measured in microns matters.
Notable features include:
- Industry-leading accuracy of ±0.0005″ (0.0127mm)—comparable to machines many times its size and price
- Automatic tool changing capability with 8-tool capacity for complex multi-operation jobs
- Rigid aluminum construction with precision linear rails for stability
- Advanced software integration with automatic material location and work coordinate setup
The Bantam Tools Desktop CNC has found particular success in industries requiring prototype development and small-batch production of precision components, including metal milling applications for specialized electrical parts.
“The revolution in small CNC machining has democratized precision manufacturing. Today’s desktop machines deliver tolerances that were once only possible with equipment costing ten times as much. This has been a game-changer for specialized component manufacturers,” says Dr. Michael Chen, Industrial Automation Specialist at the Institute for Advanced Manufacturing.
Stepcraft D.840: Versatile Workhorse for Larger Components
For operations requiring a larger work envelope while still maintaining a reasonable footprint, the Stepcraft D.840 offers an impressive balance of size and capability. This machine provides one of the largest work areas in the “small CNC” category.
What sets the D.840 apart:
- Expandable modular design allowing for future upgrades and customization
- Exceptional versatility with options for 3D printing, laser engraving, and plasma cutting attachments
- German engineering with robust construction and high-quality components
- Ability to handle larger workpieces that would exceed the capacity of most desktop machines
The Stepcraft D.840 is particularly well-suited for businesses that need to process larger components or require the flexibility to produce diverse parts without investing in multiple specialized machines. It’s become increasingly popular in the automation equipment sector for producing custom fixtures and specialized tools.
Axiom Precision AR4 Pro+: Industrial-Grade Performance
The Axiom Precision AR4 Pro+ represents the upper tier of small CNC machines, designed for businesses that require industrial-grade performance in a relatively compact package. This machine bridges the gap between desktop mills and full-sized industrial CNC centers.
Key features that justify its premium positioning:
- Heavy-duty construction with a precision-ground cast iron frame weighing over 500 pounds
- Powerful 3HP spindle capable of handling tough materials and maintaining high feed rates
- Closed-loop stepper motors with encoder feedback for enhanced accuracy and reliability
- Precision ball screws on all axes for minimal backlash and maximum repeatability
The AR4 Pro+ has become a favorite among manufacturers producing precision-engineered components that require both accuracy and durability. Its robust construction makes it suitable for continuous operation in production environments.
Tormach PCNC 440: Production-Ready Compact Solution
Rounding out our top five is the Tormach PCNC 440, a machine designed from the ground up for small-scale production environments. Unlike some competitors that evolved from hobby machines, the PCNC 440 was conceived as a production tool from its inception.
Stand-out capabilities include:
- PathPilot control system based on professional CNC controllers used in large industrial machines
- Automatic tool changer option for unattended operation and increased productivity
- Rigid dovetail ways providing excellent stability during cutting operations
- Comprehensive ecosystem of accessories and upgrades for specialized applications
The PCNC 440 has found significant adoption in facilities specializing in precision manufacturing and small-batch production, particularly in industries where component quality directly impacts product performance and safety.
Critical Features for Small CNC Machines in Precision Manufacturing
Precision and Repeatability: The Foundation of Quality
When selecting a small CNC machine for industrial applications, precision and repeatability remain the most critical factors. Unlike hobby-grade equipment, industrial applications demand consistent results across hundreds or thousands of parts.
Key specifications to evaluate include:
- Positioning accuracy – How close the machine can get to the programmed position
- Repeatability – How consistently the machine can return to the same position
- Resolution – The smallest increment the machine can reliably move
- Geometric accuracy – How well the machine maintains perpendicularity and parallelism
For specialized applications like busbar processing, where electrical conductivity depends on precise surface preparation, even small deviations can create significant problems downstream. Industrial-grade small CNC machines should maintain tolerances of at least ±0.001″ (0.0254mm), with higher-end models achieving ±0.0005″ (0.0127mm) or better.
Spindle Power and Rigidity: Enabling Efficient Production
The spindle is the heart of any CNC machine, and its specifications directly impact productivity and capability. For industrial applications, spindle power and rigidity are critical considerations.
Important spindle characteristics include:
- Power rating – Typically measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW)
- Speed range – The minimum and maximum RPM the spindle can achieve
- Torque – Particularly important for machining harder materials
- Cooling system – Air or liquid cooling affects continuous operation capability
- Tool holder interface – Common options include ER collets, ISO/BT tapers, or HSK
Machines intended for metal processing applications should feature spindles with at least 1HP for aluminum and 2HP or more for steel and harder materials. The rigidity of the spindle mounting and its bearings will also significantly impact surface finish quality and tool life.
Control Systems and Software Compatibility
The control system of a small CNC machine determines its usability, flexibility, and integration capabilities. Modern industrial applications typically require sophisticated controls that can handle complex operations.
Essential control system features include:
- Industry-standard G-code compatibility for universal program portability
- Advanced features like cutter compensation, scaling, and rotation
- Connectivity options including USB, Ethernet, and even wireless networking
- Compatibility with CAD/CAM software commonly used in industrial environments
- Macro programming capabilities for creating parametric and adaptive processes
For manufacturers engaged in automation equipment production, the control system should also support integration with broader automation systems, including robotic loaders, in-process measurement, and statistical process control tools.
Material Compatibility and Versatility
The range of materials a small CNC machine can effectively process directly impacts its utility in industrial settings. While many small machines excel with aluminum and plastics, true industrial applications often require the ability to machine harder materials.
Material processing capabilities to consider:
- Aluminum alloys – The baseline for most small CNC machines
- Steel – Including mild steel, stainless steel, and tool steels
- Copper alloys – Important for electrical components and busbar manufacturing
- Engineered plastics – Including fiber-reinforced composites
- Exotic materials – Such as titanium, Inconel, or medical-grade alloys
The ability to effectively machine copper and copper alloys is particularly important for companies involved in electrical component manufacturing, as these materials are fundamental to products like busbars and electrical connectors.
Automation and Integration Capabilities
As manufacturing continues to evolve toward Industry 4.0, the automation capabilities of small CNC machines become increasingly important. Even compact machines should offer features that enable integration into automated workflows.
Key automation features to look for:
- Automated tool changing to reduce operator intervention
- Pallet changers or multi-fixture systems for continuous production
- Probing systems for in-process inspection and adaptive machining
- Connectivity with MES and ERP systems for production tracking
- Remote monitoring capabilities for predictive maintenance
For companies specializing in automation solutions, these features are particularly valuable as they demonstrate the practical application of the technology they themselves produce.
ROI and Cost-Effectiveness of Small CNC Machines
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Returns
Investing in a small CNC machine represents a significant capital expenditure, but one that can deliver substantial returns when properly implemented. Understanding the true cost-effectiveness requires examining both immediate and long-term financial impacts.
Key financial considerations include:
AspectSmall CNC MachinesTraditional ManufacturingInitial Cost$2,000 - $15,000$50,000+Production SpeedFast for small batchesFaster for large volumesCustomizationHighLimitedSkill RequiredModerateHighWaste ReductionUp to 40%VariesFloor SpaceMinimalExtensiveEnergy ConsumptionLowHighMaintenance Costs$500-$1,500/year$5,000-$15,000/year
According to recent industry research, small businesses implementing small CNC machines report an average 35% reduction in production costs compared to traditional methods. Most importantly, the return on investment is typically achieved within 12-18 months for operations with regular use.
Calculating True Cost Per Part
Beyond the initial investment, the cost per part calculation reveals the true economic advantage of small CNC machines for industrial applications.
Factors affecting cost per part include:
- Material costs – Small CNC machines often generate less waste
- Labor costs – Reduced operator intervention and setup time
- Tooling costs – Tool life and replacement frequency
- Energy consumption – Lower energy requirements compared to larger machines
- Maintenance expenses – Less intensive maintenance requirements
- Quality costs – Reduced scrap and rework due to higher precision
For manufacturers of specialized components like those used in new energy vehicles, the precision of small CNC machines often translates to fewer quality issues downstream, further enhancing the ROI.
Space Efficiency and Facility Impact
One often overlooked benefit of small CNC machines is their space efficiency. In manufacturing environments where floor space comes at a premium, the compact footprint of these machines represents a significant advantage.
Space-related benefits include:
- Reduced facility requirements – Less floor space needed per machine
- Lower environmental control costs – Smaller area to maintain temperature and humidity
- Improved workflow – More machines can fit in the same space
- Reduced overhead allocation – Less impact on facility-related expenses
For businesses involved in precision manufacturing, this space efficiency allows for more diverse production capabilities within the same facility footprint.
Flexibility and Adaptability Benefits
Small CNC machines offer exceptional flexibility compared to larger, more specialized equipment. This adaptability has tangible financial benefits, particularly for companies that produce a variety of parts or frequently change their product offerings.
Flexibility advantages include:
- Rapid changeover between different products
- Lower setup costs for new products
- Ability to bring previously outsourced work in-house
- Capability to serve multiple markets or applications
- Reduced risk when entering new product areas
This flexibility is particularly valuable for companies in evolving industries like automation equipment and new energy vehicles, where product requirements frequently change as technology advances.
Industry Applications for Small CNC Machines
New Energy Vehicle Component Manufacturing
The NEV industry has emerged as one of the most significant adopters of small CNC machines. The precision requirements for electrical components, battery connections, and power distribution systems make these machines ideal for this growing sector.
Key NEV applications include:
- Battery terminal manufacturing – Requiring high precision for optimal electrical contact
- Cooling system components – Including precision-machined heat sinks and fluid connectors
- Structural housing elements – For battery management systems and control units
- Connection systems – For high-voltage electrical distribution networks
As the NEV industry continues its rapid growth, small CNC machines offer the perfect combination of precision, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for manufacturers at every tier of the supply chain. Companies specializing in busbar processing automation have found these machines particularly valuable for prototyping and small-batch production.
“The precision demands of NEV electrical systems have pushed small CNC technology to new heights. The machines we see today can achieve tolerances that would have required investment in equipment costing five times as much just a decade ago,” notes Sarah Johnson, Chief Engineer at Advanced Electric Propulsion Systems.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors have long been early adopters of advanced manufacturing technologies, and small CNC machines have found numerous applications in these industries.
Common aerospace applications include:
- Avionics housing components – Requiring precise dimensions and tight tolerances
- Connector blocks – For complex wiring harness interfaces
- Instrument panels and controls – With intricate features and multiple operations
- Specialized fixtures and tooling – For assembly and testing operations
- UAV/drone components – Where weight reduction is critical
The stringent quality requirements in aerospace make the precision of industrial-grade small CNC machines particularly valuable. Many aerospace suppliers have integrated these machines into their precision manufacturing processes for specialized components.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical device industry represents another ideal application for small CNC machines, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
Medical applications include:
- Surgical instrument components – Requiring biocompatible materials and flawless finishes
- Implantable device housings – With complex geometries and stringent material requirements
- Laboratory equipment parts – For analytical and diagnostic equipment
- Custom medical fixtures – For patient-specific applications
- Prototype development – For accelerated product development cycles
Medical manufacturers value the cleanliness and control offered by enclosed small CNC machines, which help maintain the sterile conditions necessary for medical device production.
Electronics and Communications Equipment
The electronics industry has embraced small CNC machines for their ability to produce intricate components with exceptional accuracy.
Electronics applications include:
- RF component housings – Where dimensional precision directly affects performance
- Heat sink manufacturing – For thermal management in high-performance computing
- Specialized connector systems – With complex three-dimensional features
- Test fixtures – For quality control and product verification
- Custom enclosures – For specialized electronic systems
The rapid evolution of electronic products requires manufacturing flexibility that small CNC machines provide, especially for companies involved in metal processing for electronic applications.
Renewable Energy Systems
Beyond NEVs, the broader renewable energy sector has numerous applications for small CNC machines in the production of specialized components.
Renewable energy applications include:
- Solar tracker components – Requiring weather resistance and precise fit
- Wind turbine control system housings – With complex internal features
- Hydrogen fuel cell plates – Demanding extreme flatness and surface quality
- Battery connection systems – Similar to NEV applications but for stationary storage
- Microinverter housings – Requiring thermal management features and weather sealing
The growing demand for renewable energy solutions has created new opportunities for precision manufacturing using small CNC machines, particularly for companies specializing in electrical component production.
Maintenance Best Practices for Industrial CNC Equipment
Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Implementing a comprehensive preventive maintenance program is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of small CNC machines in industrial settings.
Effective preventive maintenance includes:
- Daily checks – Visual inspection, cleaning, and lubrication verification
- Weekly procedures – Way lubrication, coolant concentration testing, and filter cleaning
- Monthly tasks – Belt tension verification, electrical connection inspection, and backlash checking
- Quarterly operations – Alignment verification, spindle runout measurement, and comprehensive cleaning
- Annual procedures – Calibration, bearing inspection, and complete system evaluation
Following manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules ensures consistent performance and extends machine life. For companies already involved in automation equipment manufacturing, these maintenance practices often align with their own internal expertise.
Calibration and Accuracy Verification
Maintaining the precision of small CNC machines requires regular calibration and accuracy verification procedures.
Key calibration practices include:
- Ball bar testing – For evaluating circular interpolation accuracy
- Laser interferometer measurement – For precise linear axis verification
- Spindle analyzer use – For monitoring spindle performance and bearing condition
- Thermal stability testing – To understand and compensate for thermal expansion effects
- Geometric accuracy verification – Including squareness and parallelism checking
For manufacturers involved in precision applications like busbar processing, maintaining calibration standards is essential for product quality and consistency.
Tool Management and Optimization
Proper tool management significantly impacts both part quality and operating costs for small CNC machines.
Best practices for tool management include:
- Tool life tracking – Monitoring usage hours or parts produced per tool
- Cut parameter optimization – Adjusting speeds and feeds for maximum tool life
- Tool measurement and inspection – Regular verification of tool geometry and condition
- Tool path optimization – Minimizing unnecessary tool movement and engagement changes
- Material-specific tool selection – Using appropriate coatings and geometries for different materials
Effective tool management is particularly important for automated operations, where tool failure can result in significant downtime and scrap. Companies specializing in metal milling have developed considerable expertise in this area.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, small CNC machines may occasionally experience problems. Understanding common issues and their solutions minimizes downtime.
Frequently encountered problems include:
- Surface finish issues – Often related to tool condition, spindle problems, or incorrect parameters
- Dimensional inaccuracy – Potentially caused by calibration drift, temperature variation, or mechanical wear
- Unexpected shutdowns – Frequently related to electrical issues or control system problems
- Unusual noises or vibration – Indicating potential bearing failure, imbalance, or loose components
- Communication errors – Related to software conflicts or network connectivity problems
Developing in-house troubleshooting expertise is valuable for companies heavily reliant on CNC technology. Many manufacturers in the precision manufacturing sector maintain detailed troubleshooting guides specific to their equipment.
Future Trends in Small CNC Machining for NEV Components
Integration with Industry 4.0 Systems
The future of small CNC machines lies in their integration with broader Industry 4.0 ecosystems, creating smart manufacturing environments.
Emerging integration trends include:
- Digital twin implementation – Creating virtual replicas of machines for simulation and optimization
- AI-powered predictive maintenance – Using machine learning to predict failures before they occur
- Cloud-connected operation – Enabling remote monitoring, programming, and performance analysis
- Automatic parameter optimization – Self-adjusting cutting parameters based on material and tool condition
- Integration with MES and ERP systems – For seamless production planning and tracking
For companies already involved in automation equipment, these advancements represent both challenges and opportunities as they develop next-generation production systems.
Advanced Materials Processing Capabilities
As material science continues to evolve, small CNC machines are adapting to efficiently process new and advanced materials.
Material processing trends include:
- Composite machining optimization – For carbon fiber and other engineered composites
- Ceramic processing capabilities – For technical ceramics used in electrical isolation
- Specialized alloy expertise – For high-performance metals used in NEV batteries and motors
- Ultra-precision plastics machining – For enhanced surface finishes without secondary operations
- Multi-material processing – For components combining different materials in a single setup
These capabilities are particularly relevant for NEV component manufacturers, as vehicles increasingly incorporate advanced materials for weight reduction and performance enhancement.
Automation and Lights-Out Manufacturing
The drive toward fully automated production continues to influence small CNC machine development, with enhanced capabilities for unattended operation.
Automation advancements include:
- Robotic integration – For workpiece loading/unloading and secondary operations
- In-process inspection – Using probes and vision systems to verify quality during production
- Adaptive machining – Automatically adjusting to material variations and tool wear
- Multiple machine tending – Single operator managing numerous small CNC systems
- Remote operation capabilities – Allowing offsite monitoring and control
These technologies align perfectly with the expertise of companies specializing in busbar processing automation and other automated manufacturing systems.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability has become a driving force in manufacturing technology development, including small CNC machines.
Green manufacturing trends include:
- Energy consumption optimization – With intelligent power management during idle periods
- Minimal lubrication systems – Reducing oil consumption and environmental impact
- Noise reduction technologies – For improved workplace conditions
- Compact chip management – For efficient material recycling
- Heat recovery systems – Capturing waste heat for facility heating or other processes
For manufacturers serving the NEV industry, these sustainability features complement their broader environmental mission and enhance their green manufacturing credentials.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Small CNC Machine for Your Needs
The selection of a small CNC machine for industrial applications requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including precision requirements, material processing needs, automation capabilities, and long-term cost of ownership. The machines highlighted in this article represent the current state of the art in small CNC technology, offering industrial-grade performance in compact packages.
For manufacturers in specialized industries like the NEV sector, these machines provide the perfect combination of precision, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness needed to produce critical components. As busbar processing and other precision applications continue to evolve, small CNC machines will remain essential tools in the modern manufacturing toolkit.
When evaluating options for your facility, consider not only the immediate capabilities of the machine but also its future expandability, integration potential, and alignment with your long-term manufacturing strategy. The right small CNC machine is an investment that will continue to deliver value for years to come, enabling your business to maintain the precision and quality that today’s demanding industries require.
Call to Action
Ready to enhance your precision manufacturing capabilities? At Wanfur Industry Co., Ltd, we understand the critical role that precision equipment plays in modern manufacturing. While we specialize in busbar processing automation and metal processing solutions, our expertise in precision manufacturing can help you select the right equipment for your specific applications.
Contact our team today to discuss your precision manufacturing needs and discover how our expertise in automation and precision processing can help your business achieve new levels of quality and productivity. Visit our website or call us at [your phone number] to schedule a consultation with our engineering team.
External Resources
For additional information on small CNC machines and precision manufacturing, consider these valuable external resources:
- Modern Machine Shop – Comprehensive information on CNC technology and applications
- CNC Cookbook – Technical resources for CNC programming and operation
- American Machinist – Industry news and technical articles on precision manufacturing
- Manufacturing Engineering – Research and development in manufacturing technology
- Production Machining – Focused content on CNC production techniques